Recipe for tagging volumes attached to Autoscaling Groups
November 16, 2018
Recently, I had an EC2 instance die unexpectedly. This was not a huge deal as the instance was a member of an Autoscaling Group. However, I was curious WHY it went belly-up. I was shipping the OS logs over to CloudWatch, but the logs there didn’t contain any clues. In order to understand what the root cause was I needed access to the volume that was attached to the instance when it was running. However, the volume was deleted when the instance terminated because I had not explicitly told the LaunchConfiguration to retain the volume after termination.
BlockDeviceMappings:
- DeviceName: /dev/xvda
Ebs:
VolumeSize: 8The missing piece of that CloudFormation snippet is the EBC bit for DeleteOnTermination: false If the volume had been retained, I could have mounted it to another instance and rummaged around for the cause of the termination.
The solution should be easy. Right? Just change the LaunchConfiguration to retain the volume after termination. This is where they get you. How can you tell which volume was attached to what instance after termination. I suppose you could pour through logs or CloudTrail and see if you piece things back together, but there must be an easier way.
Could we tag the volume with the InstanceId it was attached to when it was running? We could certainly manually do that, but that’s gross. Is there a provision in an Autoscaling Group to add tags to instances? Yes. Is there a provision in an Autoscaling Group to add tags to the volumes attached to instances. Nope. No, there is not. Damn.
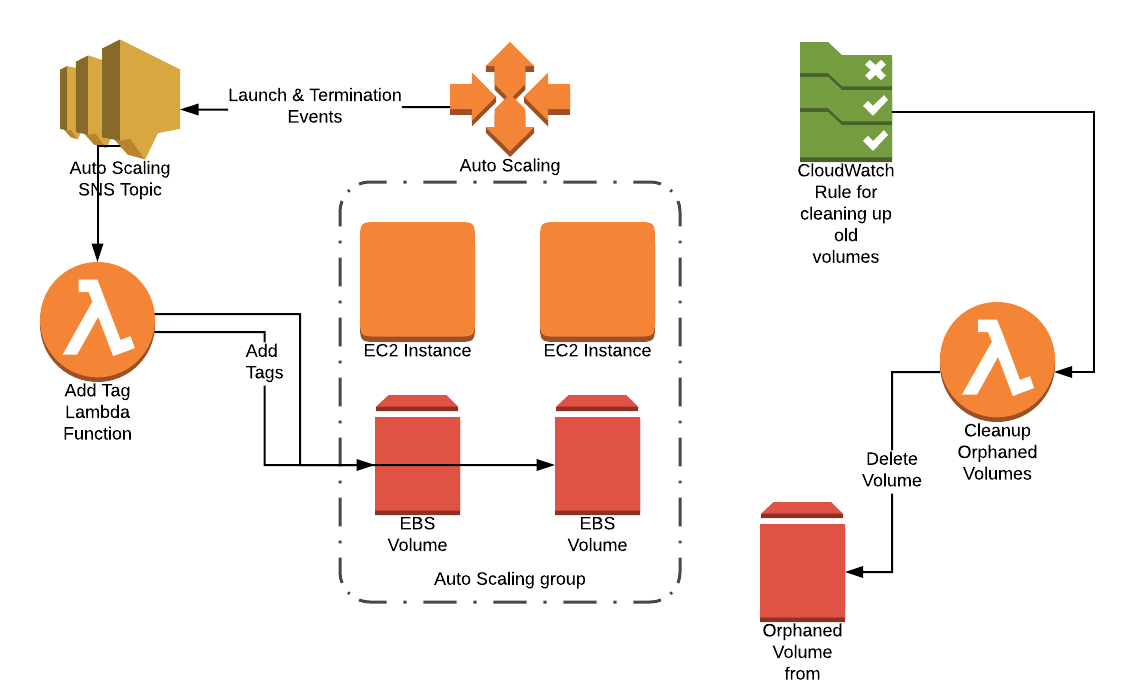
The solution
The solution is made up of two parts. One, a Lambda function that fires off SNS notifications for Autoscaling Group launch and termination events. Two, a Lambda function that is triggered from a CloudWatch Rule to cleanup any abandoned volumes after a period of time.
GitHub Repository with the entire solution.
The pieces of the solution
Security
To do all of that, we’ll need to have some IAM roles in place. Specifically, we need the ability for our Lambda functions to:
- Send logs to CloudWatch
- Describe EC2 resources
- Add tags to EC2 resources
- Delete EC2 volumes
RoleLambdaTagging:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
RoleName: EBS-Tagging-Lambda-Role
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action: sts:AssumeRole
Principal:
Service: lambda.amazonaws.com
Path: "/"
Policies:
- PolicyName: tagging
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- logs:*
Resource: 'arn:aws:logs:*:*:*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- ec2:Describe*
Resource: '*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- ec2:CreateTags
Resource: '*'
RoleLambdaCleanup:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
RoleName: EBS-Cleanup-Lambda-Role
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action: sts:AssumeRole
Principal:
Service: lambda.amazonaws.com
Path: "/"
Policies:
- PolicyName: cleanup
PolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- logs:*
Resource: 'arn:aws:logs:*:*:*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- ec2:Describe*
Resource: '*'
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- ec2:DeleteVolume
Resource: '*'Autoscaling Groups and LaunchConfig
The tagging of volumes is dependent on two pieces. The first, changing the LaunchConfiguration so the volume is not automatically deleted upon instance termination. The second, having the Autoscaling Group configured to send notifications to a SNS topic during launch and terminate events.
LaunchConfig:
Type: AWS::AutoScaling::LaunchConfiguration
Properties:
ImageId: !Ref 'ImageId'
SecurityGroups: !Ref 'SecurityGroup'
InstanceType: !Ref 'InstanceType'
KeyName: !Ref 'KeyName'
IamInstanceProfile: !Ref 'InstanceProfile'
BlockDeviceMappings:
- DeviceName: /dev/xvda
Ebs:
VolumeSize: 8
DeleteOnTermination: false
AutoScalingGroup:
Type: AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup
UpdatePolicy:
AutoScalingRollingUpdate:
MinInstancesInService: 1
MaxBatchSize: 1
PauseTime: PT1M
Properties:
AvailabilityZones: !GetAZs ''
Cooldown: '300'
DesiredCapacity: !Ref 'CapacityDesired'
MinSize: !Ref 'CapacityMin'
MaxSize: !Ref 'CapacityMax'
LaunchConfigurationName: !Ref 'LaunchConfig'
NotificationConfigurations:
- TopicARN: !Ref 'SNSAutoScale'
NotificationTypes:
- autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_LAUNCH
- autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_LAUNCH_ERROR
- autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_TERMINATE
- autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_TERMINATE_ERROR
ScaleUpPolicy:
Type: AWS::AutoScaling::ScalingPolicy
Properties:
AdjustmentType: ChangeInCapacity
AutoScalingGroupName: !Ref 'AutoScalingGroup'
Cooldown: '120'
ScalingAdjustment: 1SNS Topic
Our first Lambda function is then subscribed to the SNS topic.
SNSAutoScale:
Type: AWS::SNS::Topic
Properties:
TopicName: !Ref 'SNSTopicName'
DisplayName: Sends out alerts about autoscaling events
Subscription:
- Endpoint: !GetAtt 'LambdaAddTagFunction.Arn'
Protocol: lambdaLambda function to tag volumes
When the Lambda function fires, it evaluates the SNS message to see which type of event occurred. The script is divided by the two event types: autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_LAUNCH and autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_TERMINATE. For the launch events, the EC2 instance information is retrieved and a tag for the InstanceId is added to all the attached volumes. This tag will be useful should any forensic work need to be done after the instance is terminated. For termination events, the function finds all the instances that have the InstanceId tag for the terminated instance and then adds an additional tag for the date the instance was terminated. This tag will be used by our final function for cleanup.
LambdaAddTagFunction:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
FunctionName: 'ebs-asg-tag-new-volumes'
Description: 'Add tags to EBS volumes attached to ASG instances'
Handler: 'src/ebs-asg-tagging.lambda_handler'
Role: !GetAtt ['RoleLambdaTagging', 'Arn']
Code:
S3Bucket: !Ref 'CodeBucket'
S3Key: !Ref 'PackageKey'
Runtime: 'python2.7'
Timeout: 60
MemorySize: 128
LambdaPermissionTag:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Permission
Properties:
Action: "lambda:InvokeFunction"
FunctionName: !GetAtt ['LambdaAddTagFunction','Arn']
Principal: "sns.amazonaws.com"
SourceArn: !Ref 'SNSAutoScale'Finally we have the actual function that is being executed. In this case, I elected to use Python. It is called bs-asg-tagging.py.
import os
import boto3
import json
import logging
import datetime
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Determine the region
region = os.environ['AWS_REGION']
# Get a client for EC2
client = boto3.client('ec2', region_name=region)
# Dump the whole SNS message for posterity
logger.info(json.dumps(event))
# Extract the message from the SNS message
message = event['Records'][0]['Sns']['Message']
# Parse the JSON of the message
asg_event = json.loads(message)
# Get the instanceId that triggered this event
instance_id = asg_event['EC2InstanceId']
# Add tags for volumes upon instance termination or termination_error
if asg_event['Event'].startswith('autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_TERMINATE'):
logger.info("Dealing with a termination")
# Find all the volumes that have the terminated instance's InstanceId tag
filters = [
{'Name': 'tag:InstanceId', 'Values': [instance_id]}
]
result = client.describe_volumes(Filters=filters)
for volume in result['Volumes']:
logger.info(volume['VolumeId'] + " was attached to terminated instance " + instance_id)
ec2 = boto3.resource('ec2')
vol = ec2.Volume(volume['VolumeId'])
now = datetime.datetime.now()
tags = [
{'Key': 'TerminationDate', 'Value': now.isoformat()}
]
vol.create_tags(Tags=tags)
log_msg("Added TerminationDate tag for volume: " + volume['VolumeId'])
# Add tags for volumes upon instance launch or launch_error
if asg_event['Event'].startswith('autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_LAUNCH'):
logger.info("Dealing with a launch")
# Get all the volumes for the instance
filters = [
{'Name': 'attachment.instance-id', 'Values': [instance_id]}
]
result = client.describe_volumes(Filters=filters)
for volume in result['Volumes']:
logger.info(volume['VolumeId'] + " attached to new instance " + instance_id)
ec2 = boto3.resource('ec2')
vol = ec2.Volume(volume['VolumeId'])
tags = [
{'Key': 'InstanceId', 'Value': instance_id}
]
vol.create_tags(Tags=tags)
log_msg("Added InstanceId tag for volume: " + volume['VolumeId'])
def log_msg(msg):
print msg
logger.info(msg)Lambda function to cleanup old volumes
You don’t want to leave old volumes unused volumes laying around so we have a second Lambda function that executes on a daily schedule to remove any old volumes that are past their expiration date. A CloudWatch Rule does the triggering of the Lambda function.
CloudWatchCreationRule:
Type: AWS::Events::Rule
Properties:
Name: EBS-Cleanup-Orphaned-Volumes
Description: 'Schedule for triggering lambda: ebs-asg-cleanup-volumes'
ScheduleExpression: 'cron(0 8 * * ? *)'
State: 'ENABLED'
Targets:
-
Arn: !GetAtt ['LambdaCleanupFunction','Arn']
Id: 'ebs-cleanup-orphaned-volumes-rule'Then we have the Lambda function configuration.
LambdaCleanupFunction:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Function
Properties:
FunctionName: 'ebs-asg-cleanup-volumes'
Description: 'Cleanup orphaned volumes that were terminated from autoscaling groups'
Handler: 'src/ebs-asg-cleanup-volumes.lambda_handler'
Role: !GetAtt ['RoleLambdaCleanup', 'Arn']
Code:
S3Bucket: !Ref 'CodeBucket'
S3Key: !Ref 'PackageKey'
Runtime: 'python2.7'
Timeout: 60
MemorySize: 128
Environment:
Variables:
retention_days: !Ref 'RetentionPeriod'
Tags:
- Key: Project
Value: common
LambdaPermissionCleanup:
Type: AWS::Lambda::Permission
Properties:
Action: "lambda:InvokeFunction"
FunctionName: !GetAtt ['LambdaCleanupFunction','Arn']
Principal: "events.amazonaws.com"
SourceArn: !GetAtt ['CloudWatchCreationRule', 'Arn']Finally, we have the function itself. Again, it was written in Python but it could be written in any of the supported languages. I've called it ebs-asg-cleanup-volumes.py.
import os
import boto3
import logging
import dateutil.parser
from datetime import datetime,timedelta
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Define retention period in days
retention_days = int(os.environ['retention_days'])
# Determine the region
region = os.environ['AWS_REGION']
# Get current timestamp in UTC
now = datetime.now()
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2', region_name=region)
# Find all the volumes that have the terminated instance's InstanceId tag
filters = [
{'Name': 'tag-key', 'Values': ['TerminationDate']}
]
result = ec2.describe_volumes(Filters=filters)
for volume in result['Volumes']:
logger.info("Evaluating " + volume['VolumeId'] + " to see if it can be deleted")
ec2 = boto3.resource('ec2')
vol = ec2.Volume(volume['VolumeId'])
if vol.state == 'available':
for tag in vol.tags:
if tag['Key'] == 'TerminationDate':
# Get and parse the termination date from the tag
terminationDate = dateutil.parser.parse(tag.get('Value'))
# See if the delta between now and the termination date is greater than our retention period
if (now - terminationDate) > timedelta(retention_days):
# Delete Volume
logger.info("Volume " + volume['VolumeId'] + " should be deleted.")
vol.delete()
log_msg("Volume " + volume['VolumeId'] + " deleted.")
else:
log_msg("Volume " + volume['VolumeId'] + " should be retained.")
else:
log_msg("Volume " + volume['VolumeId'] + " is not in the correct state for deletion: " + vol.state)
def log_msg(msg):
print msg
logger.info(msg)Conclusion
Hopefully, with the OS logs being pushed into CloudWatch and having the EC2 volume persist after instance termination we can properly troubleshoot any future failures. If the underlaying VM host fails, your EC2 should automatically restart on a new host in the same AZ.